What is a melanotic lipstick? taint?
A melanotic lip macula is a well defined, oval, brown to black, flat patch in the central third of the lower lip. It is a lip stain. Also sometimes called lip balm and when multiple injuries are present, mucous membrane melanosis
What are the clinical features of melanotic lip freckle?
Generally solitary, a melanotic lip macula is seen more frequently in adult women, but it also occurs in men and young people. Occasionally the injury may be on the upper lip
The size varies from 1 to 8 mm. Once developed, the lesions generally remain unchanged in size and color. Occasionally they may have an irregular border and there may be a history of color change that can cause confusion with others. pigmented injuries including melanoma. Fortunately, melanoma is very rare on the lip (but it can happen).
Similar freckles can also occur in areas that are not exposed to the sun:
- Inside the mouth (oral melanotic macules)
- About him vulva in women (vulvar melanotic macular lip, vulvar melanosis)
- On the penis in men (melanotic penile macula, a penile lentigo).
Melanotic lip macules do not cause any symptoms, but their appearance may be a concern to the patient.
Lip melanotic macula
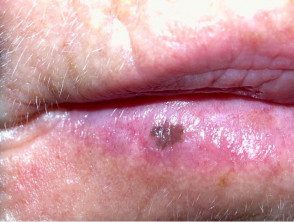
Lip melanotic macula
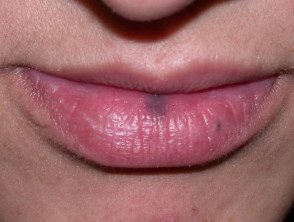
Lip melanotic macula
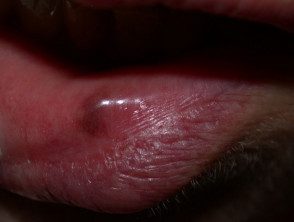
Lip melanotic macula

Lip melanotic macula
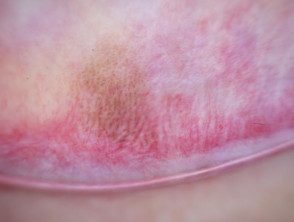
Lip melanotic macula
Lip melanotic macula
What is the cause of the lip melanotic macula?
A melanotic lip macula is believed to be caused by sun exposure, and is more common in fair-skinned people. However, it can also occur in dark-skinned individuals and, as described above, similar lesions can arise in places that are never exposed to the sun. Fortunately, melanotic macules are harmless.
What other conditions cause lip? pigmentation?
A melanotic lip macula can be confused with another pigmented skin lesion.
- Freckles (ephelides)
- Lentigo simplex
- Lentigo solar
- Venous hemangioma (venous lake)
- Amalgam tattoo
- Union melanocytic nevus (a flat mole)
- Lentigo maligna (a form of melanoma in the place)
- Superficial spreading melanoma.
These conditions can be differentiated of lip melanotic macula due to a combination of clinical and histological features.
Multiple injuries can be a sign of a extended skin condition, such as:
- Peutz Jeghers syndrome
- Addison's disease
- Laugier-Hunziker syndrome
- Multiple lentiginosis (various syndromes, including Noonan syndrome with multiple lentigines)
What research should be done?
A melanotic lip macula has a characteristic pattern when examined with a magnifying glass or by dermoscopy. Lesions with a typical history and appearance do not require a biopsy.
If a skin biopsy is performed because the lesion is changing or looks irregular, a melanotic lip macula shows the following characteristics in dermatopathology:
- Increased melanin at melanocytes and keratinocytes of the basal cap
- Melanophages at dermal papillae, which indicates pigmentary incontinence
- Mild acanthosis without lengthening the challenge ridges
Nuclear atypia is absent and the melanocyte The count is normal.
What is the treatment of lip melanotic macula?
Typical injuries can be observed. Suspicious injuries, including injuries they show progressive instead, a biopsy should be done.
If treatment is requested, the macules can be frozen (cryotherapy) or removed using a To be or intense pulsed light. Excision can also be done but will leave a scar.

