What is a exanthema?
Exanthem is the medical name given to a extended eruption that is usually accompanied by systemic symptoms like fever, discomfort and headache It is usually caused by an infectious condition, such as a virus, and represents a reaction to a toxin produced by the organism, damage to the skin by the body, or an immune response.
Exanthems
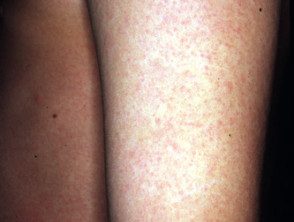
viral rash
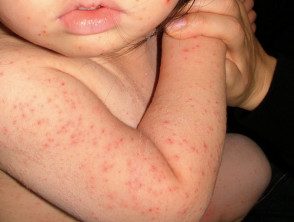
viral rash
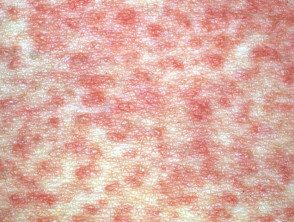
Exanthem
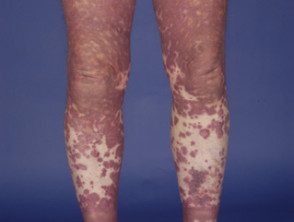
Exanthem
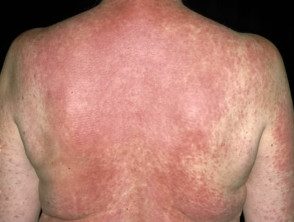
Exanthem
Exanthem
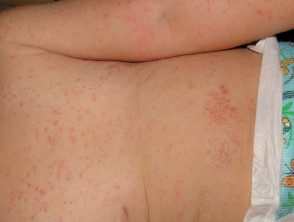
viral rash
viral rash
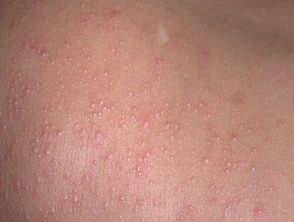
viral rash
What causes rashes?
Rashes during childhood are very common and are generally due to specific viral infections:
- Chicken pox (chicken pox)
- Measles (morbillivirus)
- Rubella (rubella virus)
Roseola (herpes virus 6B)
- Erythema infectiosum (parvovirus B19).
Viral exanthems also include:
- Acute human immunodeficiency virus infection syndrome
- Smallpox
- Viral hepatitis
Infectious mononucleosis and aminopenicillin rash (Epstein Barr virus)
- Papular purpuric gloves and socks syndrome (parvovirus B19)
- Pityriasis rosea (herpes viruses 6 and 7)
- Papular acrodermatitis of childhood.
- Erythema multiforme
- Unilateral latethoracic rash
- Some cases of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
- Nonspecific viral test.
Rashes caused by bacterial infections include:
Staphylococcal toxin infections
- Toxic shock syndrome (TSS)
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS)
- Streptococcal toxin infections
- scarlet fever
- Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome (STSS)
Other specific infections that can lead to rashes include:
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
Rickettsia diseases.
Rashes can also be caused by medication (especially antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-steroids).inflammatory drugs). See:
- Morbid drug eruption
Drug hypersensitivity syndrome.
Acute connective tissue The diseases can present with a rash.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Systemic onset youth arthritis
- Adult-onset disease
Some rashes are of unknown cause, for example Kawasaki disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of rashes?
Non-specific rashes appear as spots or blotches and may or may not be itchy. The rash is usually generalized and may be more extensive on the trunk than the extremities. In most cases, before the rash appears, patients may have symptoms of general malaise including:
- Fever
- Discomfort
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Irritability
- Muscle aches and pains.
These signs and symptoms may vary depending on the cause of the rash. See individual causes for more details. Viral exanthems often occur in small epidemics, so there may be other children affected at the same time.
Diagnosis of rashes
Many rashes have distinct patterns of eruptions and prodromal (pre-eruption) symptoms that allow clinical diagnosis.
Consult local laboratory resources to determine the most appropriate tests if in doubt, especially in a very sick patient or if the problem arises during pregnancy or immunosuppression.
Tests may include:
- Viral swab for viral culture, immunofluorescence and PCR
- Blood tests for serologyPCR RNA/ /DNA, ANA and fabric antibodies
- Genotyping
What is the treatment for rashes?
Treatment of specific rashes will depend on the cause.
Symptomatic treatment may include:
- Paracetamol to reduce fever.
- Moisturizing emollients to reduce itching

