What is paedarus? dermatitis?
Paedarus dermatitis is a skin irritation due to contact with certain species of the beetle, such as the Nairobi fly. Also known as rove beetle eruption, dermatitis linearis, spider licking, night burns and Nairobi fly rash.
A blistering rash occurs 24 to 48 hours after brushing or crushing the beetle against the skin, and may take several weeks to disappear. [1,2].
Padarous dermatitis
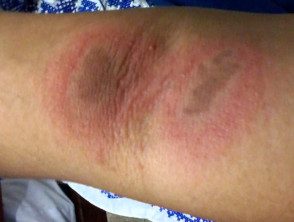
Kissing injuries
Who gets padarous dermatitis?
At least 60,000 different species of rove beetles have been identified, the largest group of insects worldwide. These insects are from the family. Staphylinidae, in the order Coleoptera (beetles) [2,3]. Beetles have narrow bodies, ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 cm. [4]. They tend to have a shiny black head and thorax, with blue or black elytra (forewings) and an orange-red abdomen. [1,4].
Rove beetles can be found in decaying plant and animal matter in most environments around the world, except Antarctica. [4]. There are over 1000 different species of rove beetles in New Zealand. They are more predominant in warmer climates [5]. The beetle's breeding period is during the rainy seasons, typically between March and April or July and August [1,4].
Padarus dermatitis is due to contact with one of more than 622 paedarus species of hedgehog beetles, which have a blistering agent in their hemolymph (hemolymph is analogous to blood in vertebrates).
Outbreaks of dermatitis paedarus are most commonly reported in Europe and Asia, but outbreaks have occurred in many other countries, including:
- Australia
- Malaysia
- Sri Lanka
- Kenya
- I ran
- Central Africa
- Uganda
- Okinawa
- Sierra Leone
- Argentina
- Brazil
- France
- Venezuela
- Ecuador
- India [2,5].
The beetle is attracted to Ultraviolet radiation (UVR); epidemics have been reported in hot regions with military units and hospital rooms with open windows and fluorescent lights [4].
Paederus beetle

Paedarus littoralis
What causes padarous dermatitis?
Padarosa dermatitis is due to pederin, a toxin produced by pseudomonas bacteria in the hemolymph and released by the female paedarus beetle [2,4,7]. Pederin causes a release of epidermal proteases and a loss of intercellular connection, inhibiting protein synthesis, DNA synthesis and mitosis [2,5].
What are the clinical characteristics of padarosa dermatitis?
A located scratched or linear erythema arises 24–48 hours after contact with the beetle and is usually followed by vesicles and pustules after 2 to 4 days [2,4,8]. Symptoms take a week or more to disappear [2]
the cutaneous Characteristics of padarus dermatitis include:
- Erythema [1,4]
- Vesicles and pustules [4,8]
- A burning sensation [1,4–8]
- “Kissing injuries” where two adjacent flexural the surfaces join [1,4]
- Periocular dermatitis and keratoconjunctivitis (“Nairobi eye”) [1,2,4,8]
- Balanitis (inflammation of the glans penis) [1,2].
What are the complications of padarosa dermatitis?
the primary The complication of padarosa dermatitis is the pain associated with the rash. Secondary complications include:
- Infection
- Exfoliation and ulceration (sometimes requires hospitalization)
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Scars [2,5].
How is padarous dermatitis diagnosed?
Pádarus dermatitis is diagnosed clinically.
- A skin biopsy from an early injury shows neutrophilic spongiosis, vesiculation and lattice necrosis of the epidermis [4]. the inflammatory infiltrate in the epidermis contains many neutrophils [4,8].
- Later biopsies show irregular acanthosis, pallor of superficial keratinocytesoverlapping parakeratosis, confluent epidermal and suprabasal necrosis acantholysis [7,8].
Which is the differential diagnosis for padarous dermatitis?
Paedarus dermatitis can be confused with:
- Herpes Simplex
- Herpes infection
- Acute allergic contact dermatitis or irritating contact dermatitis
- Phytophotodermatitis
- Bullous impetigo
- Scald
- Chemical burn
- Cutaneous larva migrans
- Herpetiform dermatitis
- Leaf Pemphigus
- Caterpillar dermatitis
- Millipede dermatitis
- Moth-related dermatitis
- Toxin-induced meloid beetle vesicular dermatitis
- Lax beetle skin disease
- Artifact dermatitis
- Trichinosis [2,5,6].
Distinctive features of paedarus dermatitis include [1]:
- Irritation limited to exposed areas.
- Kissing injuries
- Occurrence during rainy/warm season
- Other individuals who have similar injuries.
- Histopathology.
What is the treatment for padarosa dermatitis?
Once symptoms have appeared, the initial step should be to wash the affected area with soap and clean water in an effort to remove the pederin toxin.
After cleaning the area, apply a cold, wet compress and a current steroid [1].
- Tincture of iodine can help neutralize pederin and act as an antiseptic [5].
- Soothing creams containing calamine, camphor and topical anesthetic can relieve pain and itching [5].
- Oral antibiotics (eg, Ciprofloxacin) for secondary bacterial infection [7].
How can padarosa dermatitis be prevented?
Pádarus dermatitis can be prevented by limiting the possibility of exposure to the beetle.
- Use insect-proof nets at night.
- Select light sources that do not emit UV.
- Turn off the lights when you sleep.
- Remove any beetles found on the skin without crushing them.
- Wash skin in contact with a beetle with soap and water. [4,5,7].
What is the result of padarosa dermatitis?
Padarosa dermatitis may take a few weeks to resolve and post-inflammatory pigmentation it can persist for several months [1,2].

