What is acne agminata?
Acne agmina is a rare skin disorder characterized by reddish-brown lumps and bumps on the face, especially the eyelids, forehead, cheeks, and chin.[1,2] It can also affect the armpits.[3 ,4]
It was first described by Tilbury Fox as disseminated folliculitis in 1878.[1]
Other names for the disorder include:
- Lupus miliaris disseminateus faciei
- Facial idiopathic granulomas with regressive evolution
- Barthelemy's acne
- Kaposi's acne telangiectoids
- Tuberculodermas of the face [3]
- Idiopathic facial granulomas with regressive evolution (FIGURE)
Acne agminata
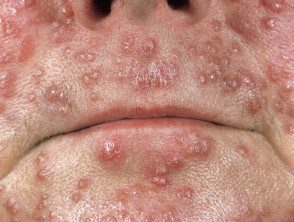
Acne agminata
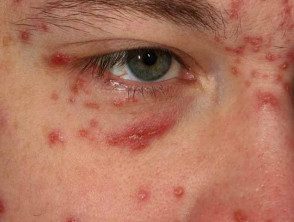
Acne agmina around the eyelid
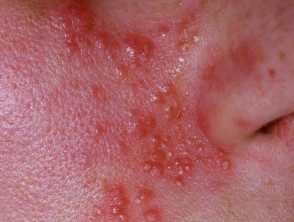
Acne agminata
* Courtesy of Dr. Anthony du Vivier.[9] ^ Courtesy of Dr Richard Logan, Princess of Wales Hospital, Bridgend, Wales, UK ->
Who gets acne agminata?
Acne agminata is most commonly found in young adults, although any age group can be affected.[5]
What causes acne agminata?
The cause and risk factors for acne agminata remain unknown. Doesn't seem to be a infection, which has been considered because granulomas are seen in histopathology.
How is acne agminata diagnosed?
Acne agminato is often a clinical diagnosis.
Typical microscopic skin changes biopsy include epithelioid granulomas within the dermis, which may be caseous even in the absence of tubercle bacilli.[3]
No further investigations are usually required once a diagnosis of acne agmina has been made, unless other diagnoses such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis (TB) are suspected, when the following tests may be considered, if appropriate.
- Blood tests: complete blood count, renal function, interferon gamma assays
- Imaging: chest x-ray
- Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux)
Differential diagnosis acne agminata
clinic and histopathological Diagnoses that should be considered include:
-
Acne vulgaris: however, comedones are absent in acne agminata, and the eyelids are usually unaffected in acne
- Rosacea
- Cutaneous tuberculosis
- Granuloma cancel
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
- Sarcoidosis
- Syphilis
What is the treatment for acne agminata?
Without treatment, acne agminata persists for 2-3 years and then returns with scarring.
Various treatments have been tried with some success, including:
- Doxycycline
- Dapsone
- Isotretinoin
- Prednis (ol) one
- Combined oral contraceptive

