What is biotin?
Biotin is an essential micronutrient. It is one of the B vitamins and is also known as vitamin H: “H” stands for “haut”, the German word for skin. Also marketed as vitamin B7 and coenzyme R
Biotin is found in many foods and is made by bacteria, fungi, algae and certain species of plants. There are particularly high amounts of biotin in brewer's yeast and royal jelly. Foods that contain the vitamin include liver, egg yolks, fish, meat, seeds, nuts, and vegetables.
Human tissues do not produce biotin, although it is produced by bacteria living in the large intestine.
Biotin acts as a cofactor for carboxylase synthetase function. enzymes. Carboxylases are enzymes that catalyze the addition of a molecule of carbon dioxide to another compound to form a carboxyl group. The carboxylase group of enzymes catalyzes fatty acid biosynthesis, gluconeogenesis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, and also plays a role in gene regulation.
What are biotin sensitive skin disease?
These are acquired or inherited problems that resolve when additional biotin is taken.
Biotin deficiency can be acquired by:
- Dragged on ingestion of raw egg whites. Avidin, a glycoprotein In the egg white, biotin binds specifically and firmly and prevents its absorption. Avidin is denatured by cooking and cooked egg whites do not cause biotin deficiency.
- Long-term “parenteral” nutrition given by intravenous infusion can also lead to biotin deficiency.
- Reduced dietary biotin intake, anti-seizure medications, chronic antibiotic use and malabsorption syndromes also reduce serum Biotin levels.
there are three rare autosomal Recessive hereditary dermatoses that respond to biotin, which can occur from inborn errors of multiple carboxylase deficiency (MCD).
- Holocarboxylase synthetase (HCD) deficiency (diagnosed in neonates)
- Biotinidase deficiency (BTD) (diagnosed in older infants)
- Defect of multivitamin sodium transporter (SMVT), which transports free biotin in the intestine, liver, kidney, and other organs.
Autosomal recessive inheritance means two abnormal genes they are bound to cause disease, one from each parent. One in four male and/or female children of the parents will be affected by the disease, but it is unlikely in other family members.
Holocarboxylase synthetase catalyzes the binding of biotin to carboxylases. Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency results in increased biotin requirement and multiple carboxylase deficiency. This results in a buildup of organic acids in the urine.
Biotinidase secreted by the pancreas and intestines catalyzes the release of free biotin from biocytin and biotin-containing peptides and recovers biotin for reuse during cellular Rotation. You also need to release bound ingested biotin for absorption. a shortage of enzyme results in a higher requirement for the vitamin than normal. Several mutations reported for biotinidase deficiency. Early manifestations in childhood are acidosis, seizures, hypotonia, developmental delay. The dermatological characteristics are the skin. eruption and alopecia, which are reversible with early initiation of treatment. (MGM Report 2015).
What are the clinical characteristics of biotin-sensitive dermatoses?
Inherited conditions that cause biotin deficiency usually present in the first few weeks of life. The main features of biotin-sensitive dermatoses are skin rash and neurological issues.
Early manifestations in childhood are acidosis, seizures, hypotonia, and developmental delay. Dermatologic features are rash and alopecia, which are reversible with early initiation of treatment. (MGM Report 2015).
the seborrheic, periorificial and intertriginous distribution of eruption is similar to dermatitis in zinc deficiency (see acrodermatitis enteropathica).
The non-specific erythematous scaly eruption is typically located to humid and periorifical areas, but they can become generalized look like psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis or ichthyosis.
The periorificial distribution is especially prominent around the eyes, nose, mouth, ears, and genitalia. Alopeciahair loss) can be seen with sparse hair, thinning of the eyebrows and eyelashes. Atrophy of lingual papillae (a smooth tongue) and blepharoconjunctivitis (red eyes) may be present.
The rash is red and scaly and sometimes there are erosions. It develops over most of the body and can resemble psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or ichthyosis. It is especially prominent around the eyes, nose, mouth, ears, and genitals. Alopecia (hair loss) and conjunctivitis (red eyes) may be present.
Infant with holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
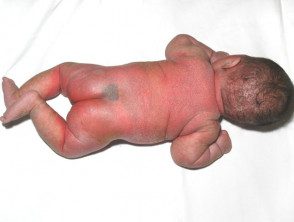
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
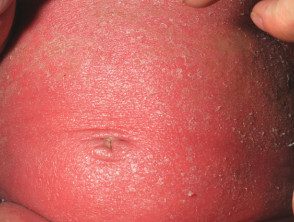
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
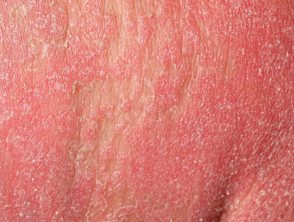
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Progressive Severe neurological symptoms develop in untreated hereditary conditions. These include seizures, failure to thrive, poor feeding, and death.
For adults with acquired biotin deficiency, the rash is similar, but neurological symptoms include hyperesthesia (sensitive skin), paresthesia (pins and needles), depression, and muscle pain.
How are biotin-sensitive dermatoses diagnosed?
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency and biotinidase deficiency are diagnosed at the neonatal and infant period, respectively, when finding high levels of organic acids in the urine. Blood tests can be done on white blood cells and plasma measure enzyme levels to confirm the diagnosis. A newborn metabolic screening can detect inherited enzyme deficiencies.
Acquired biotin deficiency is diagnosed on the clinical basis and response to treatment.
What treatment is available for biotin-sensitive dermatoses?
A biotin test should be performed in those with suspected or confirmed biotin deficiency. Usually a dosage of 10-20mg per day will be adequate. Biotinidase deficiency usually responds rapidly and dramatically to as little as 10mg per day. the cutaneous the rash usually resolves within a few weeks of biotin replacement, and hair regrowth occurs weeks to months after treatment.
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency may require much higher doses. There are reports of poor response even at 200 mg/day.
Does biotin supplementation help other skin conditions?
There are unconfirmed reports that biotin supplements may also be helpful for a rare case. congenital hair disorder called unmatched ba hair syndrome', also known as 'spun glass hair' and 'cheveux incoiffables'. Although it has been added to many cosmetic hair products, it is not clear if it is beneficial for people with normal hair.
Biotin 300 micrograms daily may also be helpful for fine brittle nails and people with lamellar splitting, but this is unconfirmed.
Biotin may be helpful in at least some cases of Leiner's disease.
In general, healthy people eating a normal diet do not require biotin supplementation for their skin, hair, or nail.
Biotin supplements can interfere with laboratory tests.
The recommended daily intake for a healthy adult is 30 micrograms (µg), but many multivitamin and biotin supplements contain much higher doses, ranging from 5,000 µg (5 mg) to 10,000 µg (10 mg). The supplements can interfere with the results of common immunoassay blood tests that use biotin technology, particularly thyroid function tests. Inaccurate test results can lead to overtreatment, undertreatment, and even death of the patient.
- thyroid stimulating hormone
- thyroxine T4 and T3
- parathyroid hormone
- troponin
- Others
If test results are not as clinically expected, the biotin-containing supplement should be withheld for 3 days before repeat testing.

