Acute presentation of a sick patient
Fever more commonly indicates bacterial or viral infection. If there is not systemic septicemia, located The rashes associated with the infection tend to cause fewer systemic symptoms than generalized rashes associated with infection. Mucous membrane Participation is common. There are some self-treblesinflammatory disorders that mimic infection due to neutrophils activation, the neutrophilic skin disease.
Consider performing the following tests:
- Swabs for bacteria and virals culture if you blister, erosions, pustules or scabs
- Blood culture if high fever
- CBC CRP
- Coagulation screen yes purple or very sick patient
- PCR and serology for specific bacteria or virus
- Echocardiography yes septic Suspicious Plungers
-
Skin biopsy of fresh skin lesions for histology, culture
The treatment depends on the cause. Consider referral to the emergency department if you suspect a serious infection or if the patient is not feeling well.
Differential diagnosis
To consider:
- Is he eruption localized or generalized? What is your distribution? Are the mucosa sites involved?
- The severity of symptoms
- Predominant morphology: is / is there erythema, blisters / erosions, pustules / crusts, purple / black areas?
Fever and localized rash
Painful, red and hot skin.
-
Cellulitis
- Unilateral swelling/hardening
- It stretches for hours to days
- There may be an associated skin disease or injury.
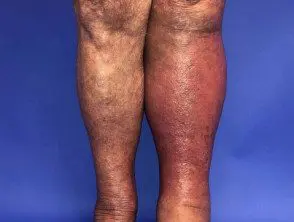
Cellulitis
-
Erysipelas
- Large one-sided plates with sharp and staggered edge
- Large blisters
- Face, lower legs or anywhere
- It stretches for hours to days
- May have associated lymphangitis (red stripe to local lymph nodes)
- Culture Streptococcus pyogenes
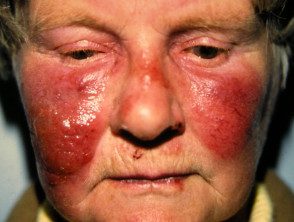
Erysipelas
-
Erythema nodosum
- Offer subcutaneous nodules
- Usually on the legs
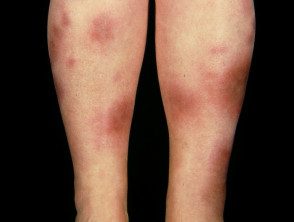
Erythema nodosum
-
Panniculitis - other
- Many causes
- Often associated with the underlying disease
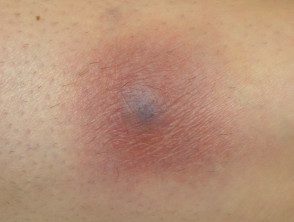
Panniculitis
Prominent blisters / erosions
-
Hand, foot and mouth
- Mainly young children
- Symmetrical vesicles mainly hands, feet and mouth
- May extend to extremities and buttocks
- Culture / PCR enterovirus
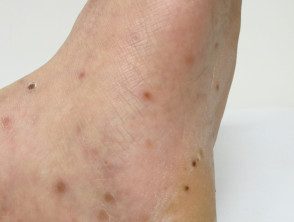
HFM in an adult
-
Herpes Simplex
- Monomorphic, umbilical vesicles, erosions, Cortex
- Culture / PCR Herpes Simplex
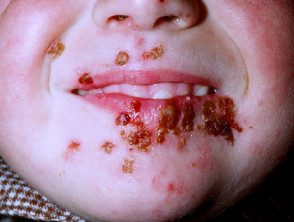
Herpes Simplex
-
Herpes infection
- Dermatomic
- Painful
- Monomorphic (early) vesicles, erosions, crusts and ulceration (late)
- Culture / PCR Herpes chickenpox-zoster
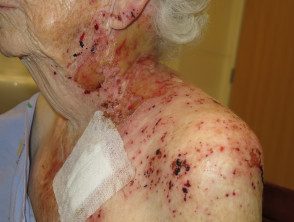
Herpes infection
-
Impetigo
- Crusted plaques, vesicles, bullaspustules
- Culture Staphylococcus aureus +/- Streptococcus pyogenes
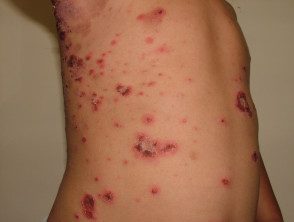
Impetigo
Pustules
-
Folliculitis / furunculosis
- based on hair follicle
- Fever without multiple boils or secondary cellulite
- Culture Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas
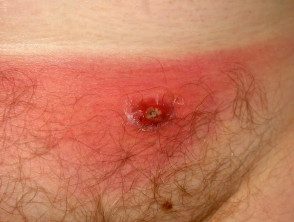
Folliculitis / furunculosis
-
Neutrophils skin disease of dorsal hands
- Dorsal hands
- Negative culture
- Confirmatory biopsy
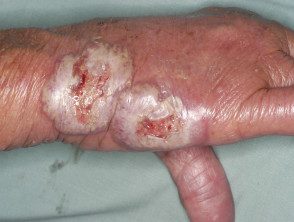
Neutrophilic dermatosis of the dorsal hands.
Purple / black areas
-
Ecthyma
- Not so bad
- It's expensive
- Small deep ulcers
- Culture Staphylococcus aureus +/- Streptococcus pyogenes
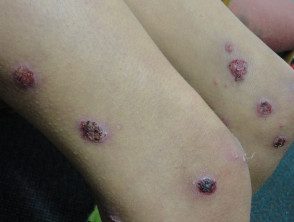
Ecthyma
-
Meningococcal disease
- Rapid state deterioration
-
Limb purpura and, more generally, limb purpura (fulminant purpura due to disseminated intravascular coagulation)
- Neck stiffness
- Light sensitive eyes.
- Got
- Blood culture / PCR Neisseria meningitidis
Withering purple
-
Necrotizing spider bite
- Endemic poisonous spiders
- The spider must be observed to make this diagnosis
- Central punctum with purple /necrosis, surrounding erythema and induration
Katipo spider bite
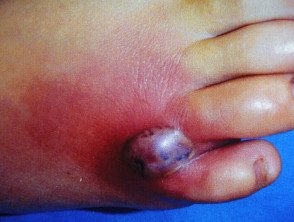
Necrotizing Spider Bite
-
Necrotizing fasciitis
- Very ill; septic shock
- Rapid spread of cellulite with purpura / blisters.
- Fournier gangrene is necrotizing fasciitis that affects the genitals
- Anesthetic areas in early lesions
- Essential bacterial culture
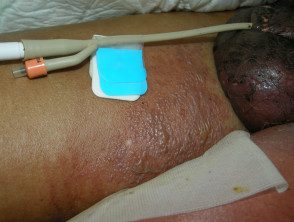
Fournier's gangrene
-
Vascular occlusion
-
Cholesterol embolism
- Recent vascular / cardiac procedure
-
Cholesterol embolism
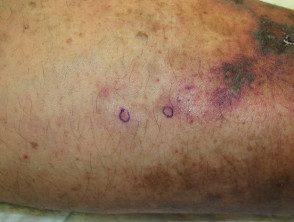
Cholesterol emboli
-
-
Septic emboli
- Endocarditis, arthritis
-
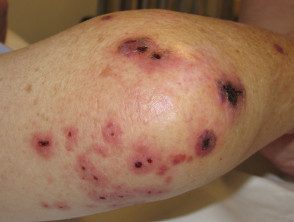
Septic emboli
-
-
Calciphylaxis
- Renal dialysisdiabetes
-
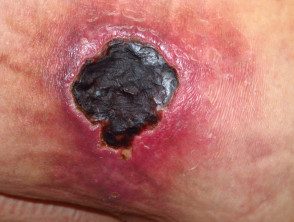
Calciphylaxis
Fever and generalized rash.
Redness
-
Drug hypersensitivity syndrome
- Morbid (maculopapular) eruption or other rash
- Drugs within 8 weeks of onset
- Other affected organs (kidney, hepaticrespiratory hematological)
- Can have eosinophilia
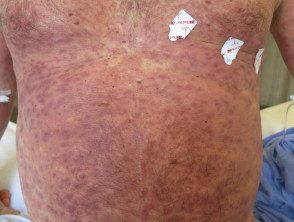
Drug hypersensitivity syndrome
-
Infectious erythema / fifth disease
- Child> adult
- Red-cheeked appearance on the cheek
- Recurrent reticulated rash on the arms.
- Serology / PCR Parvovirus B19
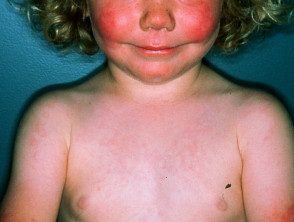
Infectious erythema / fifth disease
- Marginal erythema
- Rheumatic fever
- Evanescent cancel/ /polycyclic raised edge rash with temperature spike
- Evidence of streptococcal infection.
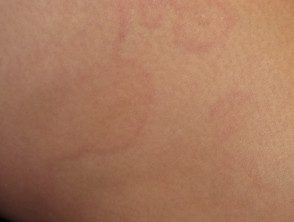
Marginal erythema
-
Erythroderma (red rash affecting> 90% of body surface)
- Preexisting atopic eczemapsoriasis
- New start: drug eruption, pityriasis rubra pilaris, lymphoma
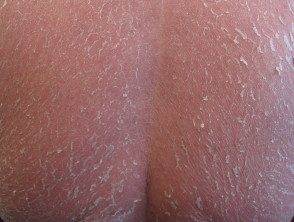
Erythroderma
-
Kawasaki's disease
- Little boy with red skin and mucous surfaces
- Swollen hands and feet.
- Peeling is a late feature
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cardiac artery aneurysms
- Another organ compromise leads to a variety of signs
- No specific diagnostic test
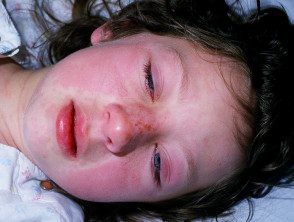
Kawasaki's disease
-
Measles
- Red eyes, red tongue, Koplik spots
- Coryza cough
- The rash has a bronze hue
- Serology / RT-PCR measles
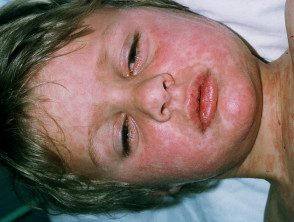
Measles
-
Unspecific exanthema
- Upper respiratory symptoms
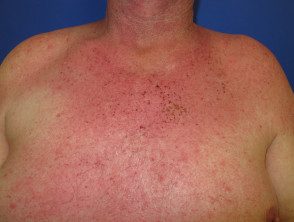
Nonspecific rash
-
Roseola / erythema subitum
- Childish
- High fever + upper respiratory symptoms
- The rash is brief
- Serology for herpes virus 6 and 7 is generally not available
-
Scarlet fever (Streptococcus pyogenes)
- Strawberry tongue
- Scarlet fever rash: tiny red macules or rough papules
- Swollen and then peeled hands
- Evidence of streptococcal infection.
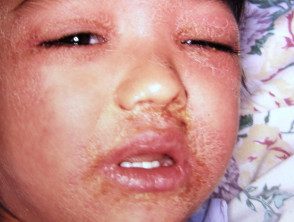
Scarlet fever
- Rare infections
-
Arbovirus (recent trip)
-
Rubella (not vaccinated)
- Typhoid fever
-
- Rare inflammatory disorders
- Various autoinflammatory syndromes.
- Often, genetic markers present
Blisters / erosions
-
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis
- Neck, limbs, upper trunk
- Pseudovesicular plates, blisters, pustules, purpura, or ulceration.
- Disease associations: rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmune arthritis, myeloid dysplasia
- Suggestive biopsy (neutrophils)
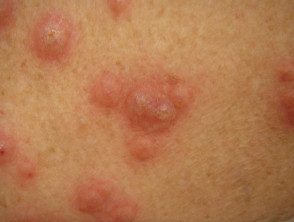
Acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis.
-
Bullous drug rash
- Blistering form of drug hypersensitivity syndrome
- Drugs within 8 weeks of onset
- Other affected organs
- You may have eosinophilia
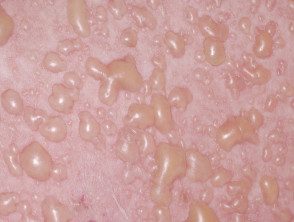
Bullous drug eruption
-
Enterovirus infection
- Mild systemic symptoms
- Vesicular eruption
- Often followed by shedding of nails
- PCR / serology enterovirus
-
Erythema multiforme
- Mainly hands, feet, face
- Target injuries
- Often preceded by herpes simplex, orf, vaccination, drugs, etc.
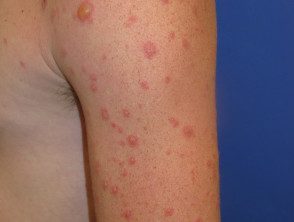
Erythema multiforme
-
Mycoplasma
-
Erythema multiforme or rash similar to Stevens Johnson syndrome
- You may or may not have pneumonia
- Serology Mycoplasma pneumoniae
-
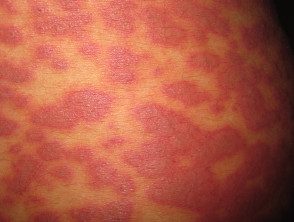
Mycoplasma
-
Staphylococcal scalded skin
- Kidney or diabetic or childhood failure
- The discomfort is slight.
- Develops from localized bullous impetigo
- Culture Staphylococcus aureus
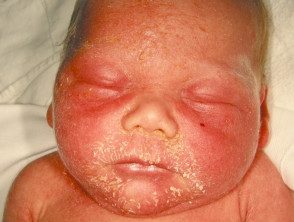
Staphylococcal scalded skin
-
Stevens-Johnson / toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Very bad patient
- Almost always drug induced
- Red skin comes out on sheets
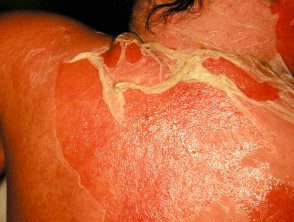
Stevens-Johnson / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
-
Chicken pox (chicken pox)
- More itching than pain
- Mainly scalp, face, trunk
- Culture / PCR Herpes chickenpox zoster
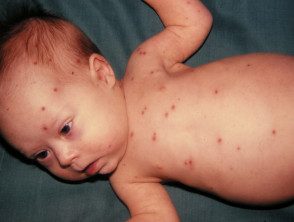
Chickenpox
Pustules / Scabs
May involve mucous surfaces
-
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)
- Drug eruption
- Suggestive biopsy
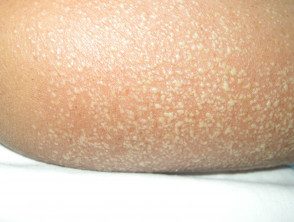
Generalized acute exanthematous pustulosis
-
Herpetic eczema
- Previous or rare eczema, other skin conditions.
- Grouped, umbilized monomorphic vesicles, pustules, or crusts
- Herpes simplex culture / PCR
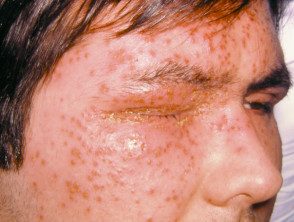
Herpetic eczema
-
Generalized pustular psoriasis (Zombusch)
- May or may not have a history of license plate psoriasis
- Symmetrical eruption of numerous superficial pustules on red skin.
- Often void, flexural
- Associated with hypocalcemia
- Suggestive biopsy
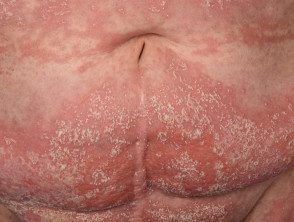
Generalized pustular psoriasis.
-
Chickenpox (late stage)
- More itching than pain
- Mainly scalp, face, trunk
- Culture / PCR Herpes varicella zoster
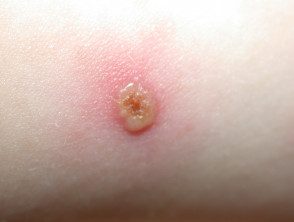
Chickenpox
Extended purple / black areas
-
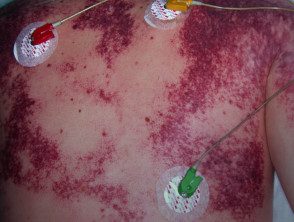
Fulminant purpura / disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Usually due to meningococcal disease (stiff neck, photophobia)
- Rapid deterioration of the mental state.
- Purple initially affects the extremities
- Blood cultures / meningococcal PCR can reveal the cause
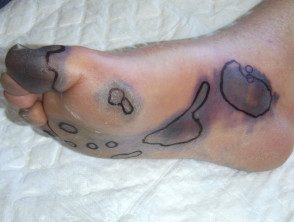
Fulminant purpura / disseminated intravascular coagulation
-
Vasculitis
- Palpable purple
- Recent or drug or underlying infection chronic disease
- Confirmatory biopsy
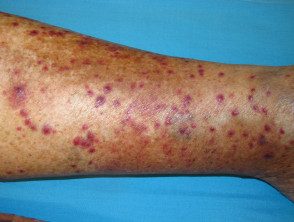
Vasculitis
