What is frnoderma?
Phrynoderma is a form of follicular hyperkeratosis associated with nutritional deficiency.
Follicular hyperkeratosis
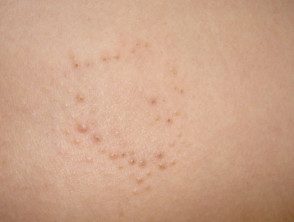
Lichen spinulosa
Who Gets Cold Derma?
Frinoderma is most often reported in children living in poverty in Africa and Asia.
A dietary history can reveal:
- Long history of poor dietary intake in the past 1 to 2 years.
- Lack of vegetables, fruits and fat in the diet.
Frinoderma is rare in developed countries, when it is most often associated with:
- Intestinal malabsorption
- Anorexia nervosa
- Fad diets
- Previous bariatric surgery or small bowel bypass surgery
- A history of alcoholism.
Frinoderma is associated with another chronic diseases, such as pancreatic insufficiency, inflammatory bowel disease and gallbladder disease [1–3].
What causes frnoderma?
Frnoderma is associated with nutritional deficiency, particularly [1,4]:
-
Vitamin A deficiency (commonly)
- Severe malnutrition
- Vitamin E and B deficiency
-
Essential fatty acid deficiency.
What are the clinical features of cold dermatitis?
Phrynoderma is a form of asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic follicular hyperkeratosis, where follicular papules of various sizes with central keratotic plugs that block the follicle openings develop in the skin [1]. New patches can be hypopigmented [3,4].
Initially, patches appear on the back of the elbows and on the front of the knees, and can spread to involve the extremities, forearms, and thighs.
Occasionally, patches will also appear on the abdomen, back, and buttocks. The face is rarely affected, and the hands and feet are spared [1].
Other symptoms of vitamin A deficiency may be present, such as:
- Night blindness
- Inability to see in bright light.
Features of severe vitamin A deficiency can include [2]:
- Xerophthalmia (dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea of the eye with inflammation and ridge formation)
- Bitot's spots (gray-white patches on the conjunctiva)
- Keratomalacia (dryness and clouding of the cornea) that can lead to blindness.
- Stunted growth
- Mental retardation.
What are the complications of cold dermatitis?
Cold derma can cause persistence hyperpigmentation or scars
How is frnoderma diagnosed?
In the correct context, chrnoderma can be suspected because of its characteristic clinical features. If a skin biopsy is interpreted, histological Features may include:
- Enlarged hair follicles containing curb plugs
- Laminated hyperkeratosis next to the hair follicles.
- Atrophy of the sebaceous glands
- Keratinizing metaplasia of epithelial surfaces
- Scaly metaplasia of eccrine and sebaceous glands, in severe disease [1,2].
The level of vitamin A in the blood of patients with frinoderma may be low (<30 μg >
The diagnosis of frioderma is compatible if the signs resolve with better nutrition. [4].
Which is the differential diagnosis of frioderma?
Several other conditions are characterized by follicular hyperkeratosis. These conditions include:
- Keratosis pilaris (small horny plugs that block hair follicles on the arms and outer thighs of healthy individuals)
-
Darier's diseasescaly papules affecting the hands and seborrheic areas, including the forehead, scalp, nasolabial folds [the laugh lines], ears and chest).
-
Lichen spinulosus (a acute eruption of grouped keratotic papules)
-
Circumscribed keratosis (a follicular form of ichthyosis)
What is the treatment for cold dermatitis?
Patients with frinoderma can be evaluated by a nutritionist, dietician, ophthalmologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist and / or general practitioner.
Nutritional management can include:
- Vitamin A replacement (50,000–150,000 U / day for 1–4 months [1])
- Foods rich in vitamin A (eg, liver, carrot, spinach, egg yolk)
- Supplemental linoleic acid with safflower or flaxseed oil (2 tablespoons, twice daily)
- Other supplements based on the results of the dietary evaluation.
Current keratolytic agents can be applied to scale plates for symptomatic relief These agents may include:
-
Salicylic acid ointment
-
Tretinoin gel or cream
-
Urea cream.
What is the result of cold dermatitis?
Skin lesions can take 1 to 4 months to resolve with restoration of nutrition. Topical keratolytic medications can provide temporary relief [3,4].
Vitamin A deficiency can cause ocular disturbance, but this usually resolves within a few days of starting therapy, unless scarring has occurred. If left untreated, there may be permanent scarring on the conjunctiva and cornea. [3,4].

