What is it pyogenic granuloma?
Pyogenic granuloma is relatively common, reagent proliferation of capillary blood vessels. That It appears as a bright red lump with a surface similar to raspberry or minced meat. Although they are benignpyogenic granulomas it can cause discomfort and profuse bleeding.
Pyogenic granuloma is also called lobular capillary. hemangioma, granuloma pyogenicum and granuloma telangiectaticum.
Pyogenic granuloma

Pyogenic granuloma
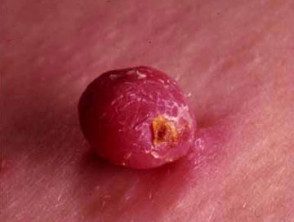
Pyogenic granuloma
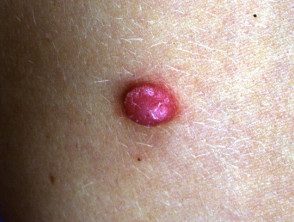
Pyogenic granuloma
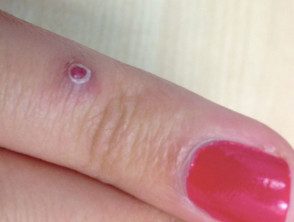
New injury
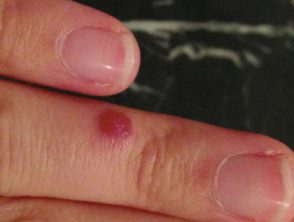
2 weeks later
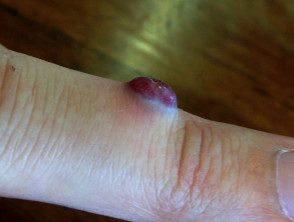
4 weeks after the first photograph
What Causes Pyogenic Granuloma?
The cause of pyogenic granuloma is unknown. The following factors have been identified to play a possible role in its development.
- Trauma- Some cases develop at the site of a recent minor injury, such as a puncture.
- Infection: Staphylococcus aureus is frequently present in the injury.
- Hormonal influences: they occur in up to 5% of pregnancies and are sometimes associated with an oral contraceptive.
- Drug induced; sometimes multiple lesions develop in orally treated patients retinoid (acitretin or isotretinoin) or a protease inhibitor.
- Viral infection is possible but not proven.
Who gets pyogenic granuloma?
Pyogenic granuloma affects people of all races. Women are affected more often than men due to the relationship with pregnancy. It rarely occurs in children younger than 6 months, but is common in children and young adults.
What are the signs and symptoms of pyogenic granuloma?
Pyogenic granuloma usually first appears as a painless red, reddish-brown, or bluish-black patch. It grows rapidly over a period of a few days to weeks to a final size of 1 to 2 cm (rarely up to 5 cm). It usually bleeds easily and can ulcerate to form a crusty sore. Usually there is a single injury, but in rare cases multiple injuries may develop.
They are most often found on the head, neck, upper torso, hands (especially fingers), and feet. The pregnancy variant of pyogenic granuloma occurs most frequently in the mucous membrane surfaces of the lip or inside the mouth.
How is pyogenic granuloma diagnosed?
Pyogenic granuloma is usually diagnosed clinically because of its typical appearance and time course.
Histology confirms the diagnosis, especially if a skin form Cancer how amelanotic melanoma it's in the differential diagnosis. Pyogenic granuloma reveals a lobular collection of blood vessels within inflamed tissue.
What treatment is available for pyogenic granuloma?
Pyogenic granulomas can go away on their own, particularly those associated with pregnancy. If it is due to a drug, they usually go away when the drug is stopped.
There are several methods used to remove pyogenic granuloma.
- Surgical excision
-
Curettage and cauterization: the lesion is scraped off with a curette and feeding blood vessel cauterized to reduce the chances of re-growth.
- To be Surgery can be used to remove the lesion and burn the base, or a pulse dye laser can be used to reduce small lesions.
- Cryotherapy May be suitable for small injuries.
- Chemical cautery with silver nitrate is effective for small lesions.
-
Imiquimod cream It has been reported to be effective and may be particularly helpful in children.
- Experimentally, current 1% from propranolol ointment has been shown to be effective when used early in children with pyogenic granuloma [1].
Reappearance after treatment is common because the feeding of the blood vessels extends deep into the dermis conical in shape. In these cases, the most effective method of removal is to completely cut the affected area (excision), which is then closed with stitches.

