What is Noonan? syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is common autosomal dominant disorder associated with mutations in the Ras / mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and is one of a group of conditions that are collectively known as RASopathies.
Noonan syndrome is characterized by:
- A distinctive facial appearance
- Short stature
- Chest deformity
- Congenital heart disease.
Noonan syndrome is also known as:
- Family Turner syndrome
- Female pseudo-Turner syndrome
- Male Turner syndrome
- Noonan-Ehmke syndrome
- Pseudo-Ullrich-Turner syndrome
- Turner syndrome
- Turner phenotype with normal karyotype
- Ullrich-Noonan syndrome.
A 12-year-old girl with Noonan syndrome.
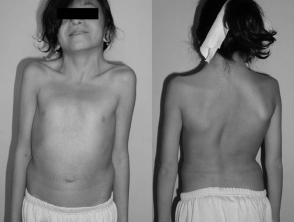
Noonan syndrome
Source: Wikipedia
What Causes Noonan Syndrome?
Noonan syndrome is caused by mutations in the genes associated with the Ras / MAPK cell signaling pathway, which is required for normal cell division, proliferation, differentiation and migration. These mutations lead to loss of regulation of cell growth and division.
Mutations in PTPN11 gene are involved in more than 50% of Noonan syndrome cases. Genetic mutations in SOS1 are involved in the 10-15% of cases and mutations in the RAF1 gen and the RIT1 The genes represent approximately 5% each. Several other genes make up the rest.
the genetic The cause of Noonan syndrome is unknown in up to 20% of cases.
What are the clinical features of Noonan syndrome?
Noonan syndrome both sexes and all races; 50-70% of people with Noonan syndrome are short. Birth weight and length are usually normal, but growth slows over time. This is believed to be associated with abnormal levels of growth hormone.
Noonan syndrome presents with distinctive facial features, such as:
- Deep filter (groove between nose and mouth)
- Hypertelorism (eyes wide apart)
- Low ears turned back
- High arched palate
- Poor alignment of teeth
- Micrognathia (small lower jaw).
Other clinical manifestations of Noonan syndrome include:
- A webbed neck
- A short / low neck later hairline
- Pectus excavatum (sunken sternum) or pectus carinatum (protruding sternum)
- Scoliosis (abnormal side curvature of the spine)
- Lymphedema
- Bleeding disorders
- Hypogonadism (defective function of the gonads that can lead to insufficient production of sex hormones).
Congenital heart disease is common in most cases of Noonan syndrome, being the most common defect pulmonary valve stenosis.
Cutaneous The symptoms of Noonan syndrome are varied and the literature on the subject is limited. The documented skin effects of Noonan syndrome include:
- Pigmented melanocytic naevi (moles)
- Abnormal dermatoglyphs (fingerprints), with a greater number of spirals appearing on the fingertips, secondary to peripheral lymphedema
-
Stasis dermatitis (a common inflammatory skin disease, because venous grouping in the lower extremities).
- Plant hyperkeratosis or keratoderma (thickening of the skin on the soles of the feet).
Noonan syndrome with multiples lentigines, formerly known as LEOPARD syndrome, is similar to Noonan syndrome. It has characteristic skin characteristics, including:
-
Coffee with milk macules (flat, light brown macules) caused by a collection of pigment-producer melanocytes at epidermis
-
Lentigos (flat or slightly raised pigmented lesions with well defined edges): Unlike freckles, these spots are not affected by sun exposure.
What are the complications of Noonan syndrome?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy it is common in individuals with critical congenital pulmonary valve stenosis.
People with Noonan syndrome have an eight times greater risk of developing hematological malignant tumors, the most common being leukemia.
What is the treatment for Noonan syndrome?
There is no specific treatment for the syndrome. Any complications such as heart disease should be monitored and treated according to symptoms, signs, and the results of investigations.

