Which is the complement system?
Complement is part of the innate immune system.
Complement incorporates proteins, which circulate in the blood in their inactive form, and some cell membrane receptors [2]. Proteins are synthesized mainly by the hepatocytes in the liver
Complement components are systematically named alphanumerically: C1, C2, C3, C3a, C3b, C4, C4a, etc.
There are three ways to activate the plugin system:
- The classic pathway, which has two components, globulin (C1) and albumin (C2)
- The alternative paths
- Lectin binding to mannose.
All three pathways culminate in the conversion of C3 to C3 convertase [2].
Skin conditions associated with complement defects.
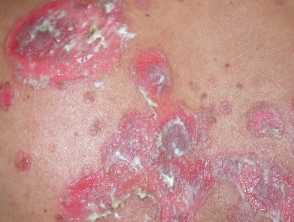
Pemphigus vulgaris
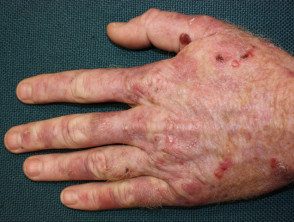
Cutaneous porphyria delays
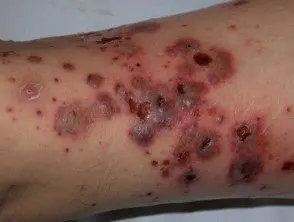
Cutaneous vasculitis
The way of the classic complement
When a antibody joins a antigen, forms an antigen-antibody immune complex, and this activates the classical complement pathway.
C1 is a protein complex composed of C1q, C1s and C1r subunits.
- Complement is activated when an immune complex binds to C1. Please note that only IgM and IgG antibodies can join C1.
- This causes a conformational change in C1, which in turn causes C2 to become activated and split into C2a and C2b, and to split C4 into C4a and C4b.
- C2b and C4b join to form a complex called C3 convertase.
- C3 convertase converts C3 to C3a and C3b.
- C3a binds to the membranes of mast cells and basophils, which triggers histamine release of cells.
- Histamine causes increased vascular permeability and recruit others immune cells to the site of infection.
- C3b has 2 functions: it acts as an opsonin to coat cells to alert phagocytes to the cell and makes it easier for these cells to gobble pathogens. It binds to C5, which makes it easier for the C3 convertase to bind to C5.
- C3 convertase binds to C5; C3b that divides C5 into C5a and C5b.
- C5a stimulates the release of histamine and stimulates chemotaxis.
- C5b stimulates the formation of the membrane attack complex.
The complement pathway
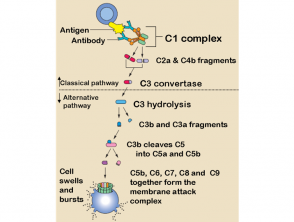
The complement pathway
The membrane attack complex
The membrane attack complex is composed of C5b, C6, C7 and C8.
- This complex binds to the cell surface of a pathogen.
- It creates a hole in the cell membrane and is surrounded by C9.
- The contents of the cell leak out and the cell is smoothed out and destroyed. [3].
The alternative path
The alternative route does not require an antigen-antibody complex.
C3 spontaneously converts to C3a and C3b.
- In the absence of pathogens, these proteins are degraded. [2].
- If there is a pathogen, C3b binds to a protein in the blood called factor B, forming a C3b-Bb complex.
The C3b - Bb complex does 2 things:
- It is a C3 convertase and activates C3 to form more C3b, thus amplifying the cascade of events.
- It can activate C5 to form the membrane attack complex.
Mannose binding lectin
A lectin is a protein that binds sugars like mannose.
The mannose-binding lectin pathway involves 2 proteins:
- Mannose binding lectin (MBL), which does not require antibodies to activate complement; Y;
- Serine proteinase associated with lectin that binds to mannose (MORE P)
MBL binds mannose on the surface of bacteria, which causes a conformational change in the MBL structure that allows MASP to divide C2 into C2a and C2b, and divide C4 into C4a and C4b [4].
C2b and C4b form C3 convertase and amplify the complement system (see alternative pathway).
How is the complement system regulated?
There are regulators to prevent the complement system from constantly activating.
- The C1 inhibitor inhibits C1 and regulates the activity of the classical pathway.
- Factor I deactivates C3b.
- Factor H inactivates the Bb protein and prevents the formation of the C3b-Bb complex [4].
What skin conditions involve defects in the complement system?
Several skin conditions are associated with defects in the complement system. [3].
Blistering diseases of the skin.
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Gestational pemphigoid
- Dermatitis herpetiform
- Porphyrias
Vascular diseases
- Urticaria
- Angioedema
- Cutaneous vasculitis
Other inflammatory diseases
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Psoriasis
How are complement tests used for diagnosis?
Complement levels can be measured by adding a serum shows in a solution with antigens. Any antibody binds to antigens to form an immune complex that precipitates out of solution.
Components of the complement system are heat labile, therefore samples sent for complement testing must be handled with care. An abnormal result may be due to mishandling during the transport of the sample.

