What is fulminant acne?
Fulminant acne is a rare and very serious form of acne conglobata associated with systemic Symptoms Almost always affects teenage boys.
Fulminating acne
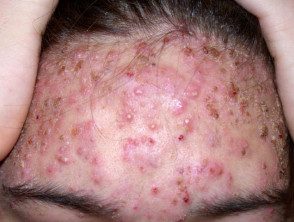
Severe acne of the forehead
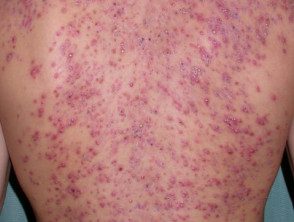
Severe acne on the back
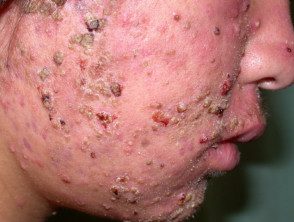
Crusted facial acne
What are the clinical characteristics of fulminant acne?
Fulminant acne is characterized by:
- Abrupt start
- Inflammatory and ulcerated nodular acne on the chest and back, which is painful
- Bleeding crusts on the ulcers in the upper trunk
- Scars from severe acne
- Fluctuating fever
- Painful joints, including sacroiliac joints in 20% of cases, ankles, shoulders and knees.
- Discomfort (i.e. the patient feels bad)
- Loss of appetite and weight loss.
- Enlarged liver and spleen.
Tests generally reveal:
- Anemia (gone down hemoglobin tell)
- High white blood cell count
- High erythrocytes sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein levels
- X-rays can show osteolytic bone lesions.
What causes fulminant acne?
Fulminant acne has been associated with an increase androgens (male hormones), autoimmune complex disease and genetic predisposition. It may be related to an explosive. hypersensitivity reaction to the surface bacteria (Cutibacteria acnes) Fulminant acne can be precipitate by:
- Testosterone and anabolic steroids (legally prescribed or taken illegally to improve muscle growth)
- Oral isotretinoin.
the syndrome SAPHO (synovitis, acne, Pustulosis, Hyperostosis and osteitis) can be a serious complication of fulminant acne.
What is the treatment for fulminant acne?
Patients with fulminant acne should consult dermatologist urgently. Management can be difficult, and multiple medications are generally required for several months or more. These may include:
- Systemic corticosteroids such as prednisone (20–60 mg / day)
- Anti-inflammatory medicines like salicylates (aspirin)
-
Dapsone 50–100 mg / day
- Cyclosporine
- High doses of oral antibiotics such as erythromycin (2 g / day) for secondary infection
-
Isotretinoin started at low doses after control has been obtained with systemic steroids
- Tumor necrosis alpha factor inhibitors (TNF-α), such as infliximab.
Current Acne medications are not helpful.

