What is myeloma?
Mycetoma is a chronic infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Sometimes it can also affect the muscles, bones, tendons, and joints.
Mycetoma is characterized by nodules and breast treaties that download watery fluid or pimples that contain pus [1].
Mycetoma is classified as:
- Eumycetoma: when it is caused by a fungus;
- Actinomycetoma: when caused by filamentous bacteria of the order, actinomycetes.
Mycetoma
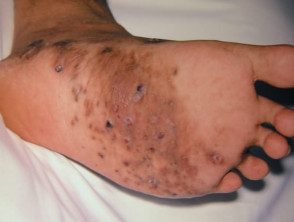
Mytoma foot
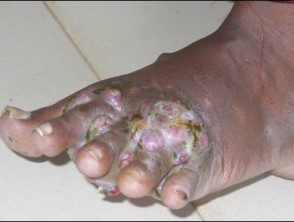
Courtesy of Dr. Sriyani Samaraweera
Actinomycetoma due to nocardia
Who gets mycetoma?
The bacteria and fungi that cause myeloma have a worldwide effect. distribution in soil and plant material, but mytoma is found primarily in tropical areas in South and Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa. Most cases are reported in the “transcefrican mycomeoma belt” from West Africa, including Senegal and Sierra Leone, to East Africa, including Somalia and Sudan [2,3].
Infection usually occurs after local trauma.
- Eumycetoma mainly affects middle-aged men who work as herdsmen or farmers, especially when they walk barefoot.
- Mycetoma can also affect younger men and women.
- Actinomycetoma can also be related to oral infections, teeth, or gum disease.
Mycetoma is unaware vector or animal reservoir, and there are no reports of human-to-human transmitted infections [1,3].
What Causes Myeloma?
The causative agent can be suspected from the color of the pimples.
Eumycetoma
Dark or black pimples
- Madurella mycetomatis
- Trematosphaeria grisea (before Madurella gray)
- Exophiala jeanselmei
- Medicopsis romeroi (before Pyrenochaeta romeroi)
- Falciformispora senegalensis (before Leptosphaeria senegalensis)
- Falciformispora thompkinsii
- Curvularia lunata
White grains, buckets or undyed
- Acremonium spp.
- Fusarium spp
- Neotestudina rosatii
- Aspergillus nidulans
- Aspergillus flavus
- Microsporum ferrugineum
- Microsporum audouinii
- Microsporum langeronii
- Scedosporium apiospermum
- Scedosporium boydii (before Pseudallescheria boydii)
Actinomycetoma
White to yellow pimples
- Nocardia brasiliensis
- Nocardia otitidiscaviarum (before Nocardia caviae)
- Actinomadura mature
- Pleurostomophora ochracea
Brown grains
- Streptomcyes somaliensis
Red to pink beans
- Actinomadura pelletieri
What are the clinical features of mycetoma?
the incubation time after inoculation of the microorganism until myeloma is diagnosed varies from months to years [2].
Actinomycetoma and eumycetoma have similar clinical features. However, actinomycetomas tend to be more aggressive and destructive, invading the bones earlier.
- Mycetoma begins as a located swelling at an exposed site; two-thirds arise in the foot.
- The affected area has a normal skin temperature and often hyperpigmented.
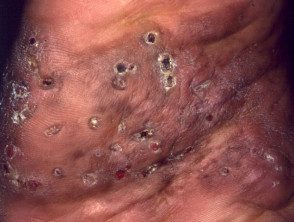
- Multiple firm nodules appear and begin to drain spontaneously or after pressure.
- Fluid discharged from the sinus tract may contain the characteristic granular grains.
- Local pain is mild or absent, and worsens only in later stages with more damage to the subcutaneous tissue or with secondary bacterial infection.
Mycetoma has little effect on the general condition of the affected patient and fever it is rare [2].
Actinomycetoma
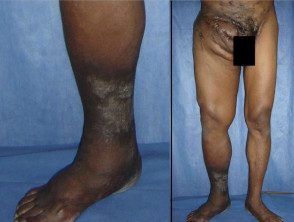
Actinomycetoma of feet and legs
What are the complications of mycetoma?
Complications of mycetoma include:
- Secondary bacterial infection
- Strange massive swelling with deformity
- Joint ankylosis and loss of function.
- Chronic edema
- Atrophy of the disused limb (reduction in size and strength)
- Pain.
These can be prevented through early diagnosis and proper treatment. [4].
How is myeloma diagnosed?
Mycetoma is suspected when there is a typical triad of symptoms and signs:
- A firm, painless subcutaneous mass.
- Multiple sinus pathways
- A purulent or seropurulent discharge that contains pimples.
Dermoscopy can be helpful in the early stages of the disease to detect pimples within skin lesions. [5]. Grains are conglomerates of fungi or bacteria arranged radially (like the sun's rays).
Fabric for microscopy and culture is collected by:
- Making a little incision and expressing secretions;
- Using a needle and syringe to draw fluid.
The color of the grains can reduce the options of the culprit. bacterium u fungus. Grains are treated with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and then stained with Gram and PAS stains. In microscopy:
- Actinomycotic grains have very fine filaments.
- Eucotic grains contain thicker branched filaments.
As some grow slowly organisms, cultures at 25–30 ° C and 37 ° C are established for up to 6 weeks for bacteria and fungi [1,6]. When it is difficult to identify the person responsible organism, molecular techniques like PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) can be used [2].
Skin biopsy can show typical histopathological characteristics of myoma.
Images can be used to assess the depth of infection. [6].
- Plain radiography
- Ultrasound scan
- Computed tomography (Connecticut)
- Nuclear magnetic resonance image (Magnetic resonance)
H&E staining of actinomycosis pimples
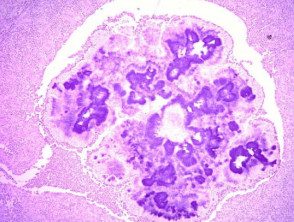
H&E staining of actinomycosis pimples
Which is the differential diagnosis for myeloma?
Infectious diseases
-
Bacterial infection: leprosy, cutaneous tuberculosis, nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, botryomycosis (non-actinomycetic bacteria that cause skin infection with pimple-like structures), syphilis, osteomyelitis
-
Fungal infection: chromoblastomycosis, sporotrichosis, and dermatophyte pseudomycetomas
Non-infectious diseases
-
Podoconiosis or other forms of mossy foot due to lymphedema
- Certain cancers: sarcoma of the skin Soft fabric or bones, Kaposi's sarcoma
- Foreign body reactions
What is the treatment for myeloma?
Mycetoma cannot be cured without active treatment. It requires antibiotics (for actinomycetomas) or oral antifungals (for eumycetomas) for weeks, months, or years. Damage to subcutaneous tissues (muscles, bones, joints, or tendons) often persists, so local surgery (including amputation) and physical therapy may be necessary. [1,2].
Actinomycetoma (individual or in combination)
- Trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole
- Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid
- Amikacin or gentamicin
- Doxycycline or minocycline
- Penicillin
- Dapsone
- Streptomycin
- Rifampicin
Eumycetoma (only one commonly used)
- Ketoconazole
- Itraconazole
- Terbinafine
What is the outcome for myeloma?
Despite the need for prolonged treatment, forecast generally good with proper therapy. The longer the infection has been present before treatment, the more likely complications and disability are [4].

