What is it cutaneous tuberculosis?
Cutaneous tuberculosis (TB) is essentially an invasion of the skin by Mycobacterial tuberculosis, the same bacteria causing TB of the lungs (pulmonary TUBERCULOSIS). Cutaneous TB is a relatively rare form of extrapulmonary TB (TB infection of other organs and tissues). Even in countries like India and China, where TB still occurs commonly, skin outbreaks are rare (<0.1%).
Types of cutaneous tuberculosis
There are several different types of cutaneous TB. Direct skin infection or mucous membranes from an external source of mycobacteria result in an initial injury called the tubercular chancre. Cankers are firm and shallow. ulcers With a granular base. They appear about 2-4 weeks after the mycobacteria enter through the broken skin. The patient's immune response and the virulence of the mycobacteria determine the type and severity of skin tuberculosis.
| Types of cutaneous tuberculosis | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| TB verrucosa skin |
|
| Vulgar lupus |
|
| Scrofuloderma |
|
| Miliary tuberculosis |
|
| Tuberculous |
|
Cutaneous tuberculosis
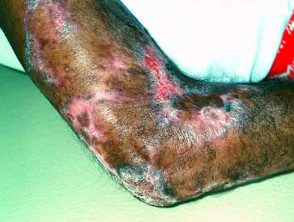
Vulgar lupus
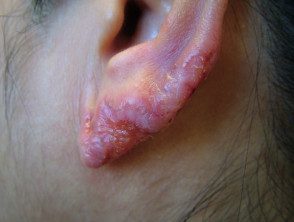
Vulgar lupus
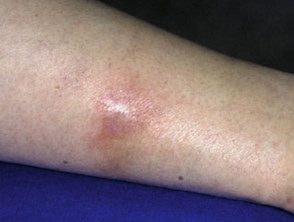
Erythema induratum
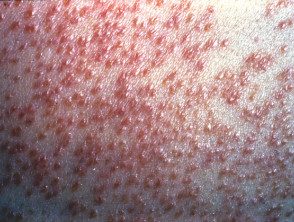
Miliary cutaneous tuberculosis
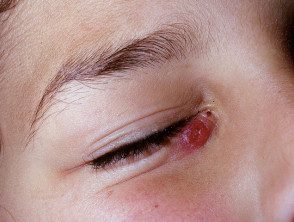
Tuberculosis innovation
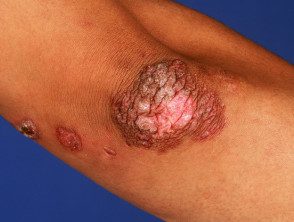
Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis
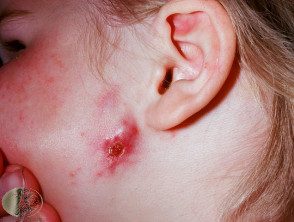
Scrofuloderma
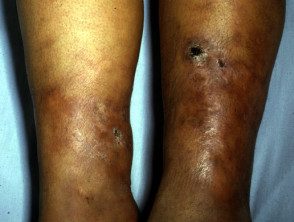
Erythema induratum
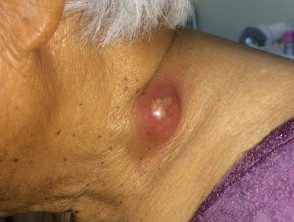
Scrofuloderma
See more images of tuberculosis ...
What tests are available?
The diagnosis is usually made or confirmed by characteristics histopathological features on the skin biopsy. Typical tubers are caseating epithelioid granulomas containing acid-fast bacilli. These are detected by tissue staining, culture and Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Other tests that may be necessary include:
- Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux test or PPD)
- Gamma interferon release assay blood test
- Sputum culture (may take a month or more for results to be reported)
- Chest X-ray and others radiological extrapulmonary infection tests.
- Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRA)
Severe Mantoux test reactions (active TB)
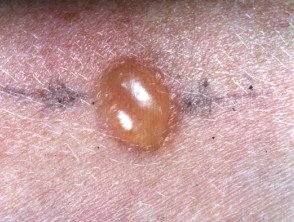
Mantoux test reaction
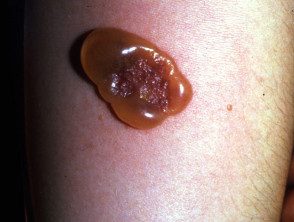
Mantoux test reaction
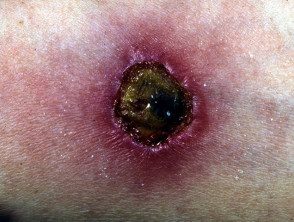
Mantoux test reaction
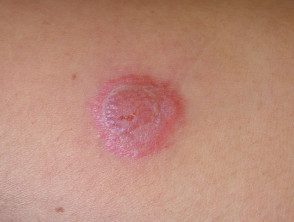
Mantoux test reaction
What is the treatment for skin tuberculosis?
Patients with pulmonary or extrapulmonary tuberculosis should be treated with antituberculous drugs. This usually involves a combination of antibiotics (isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol) given over a period of several months, and sometimes years.
Patients with latent TB infection but without active disease can also be treated with anti-TB drugs to prevent the development of active disease. See tuberculosis test.
Occasionally surgical excision of located Cutaneous TB is recommended.

